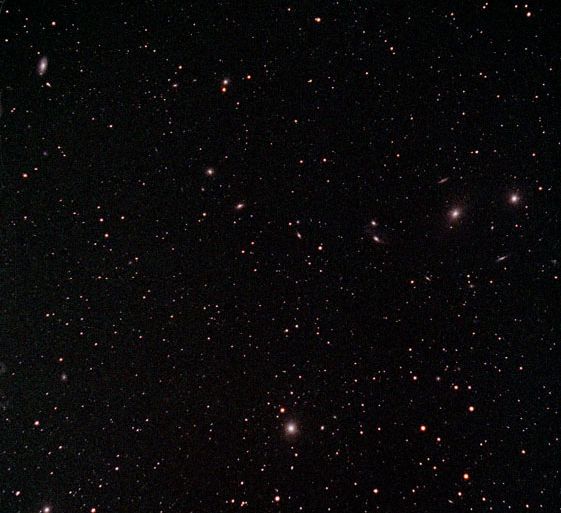

(Selected as a NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day)
Look how the sky between the stars appears dark. If the universe were infinitely big and infinitely old, then the whole sky should appear to glow.
Why isn't the night sky uniformly bright?
In the 19th century, an astronomer named Heinrich Olbers stumbled on a contradiction that could not be easily explained: why doesn't the night sky look uniformly bright? A sky that is uniformly bright would appear to glow, yet our night sky appears black with a scattering of stars, planets, and galaxies dotting the observable sky.Why do we expect the night sky to appear uniformly bright in a Steady State Universe?
To illustrate, Steady State theory is based on three previously-mentioned assumptions: the universe is
Let's examine this a little more closely.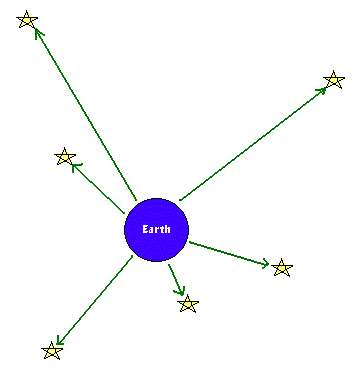
 Go Back
Go Back Next
Next